Synthetic fibers are low-molecular compounds in coal, petroleum, and natural gas. They are used as raw materials to form polymer compounds through polymerization. They are dissolved or melted to form a spinning solution, which is then jetted from the spinning orifices and solidified to form fibers. Synthetic fiber has the advantages of high production efficiency, abundant raw materials, many varieties, good taking and wide use, etc. Therefore, it has developed rapidly. At present, there are mainly seven polyesters, such as polyester and acrylic, which are used in apparel. They have the following common features:
1 The fiber uniformity is good, and the length, fineness, and cross-sectional morphology can be controlled as needed. Different cross-section fibers produce different properties such as gloss, durability and warmth retention.
2 Poor hygroscopicity, fabrics are easy to wash and dry, no shrinkage, good washability, but not as hot and humid comfort as natural fibers, easy to electrostatic, easy to attract dust.
3 Most synthetic fibers have strong strength, large elongation capacity, good elasticity, good abrasion resistance, and they are made of durable, good conformability and are not easy to wrinkle. Synthetic fiber filament fabric is easy to hook silk, synthetic fiber staple fiber fabric is easy to pilling.
4 The chemical stability is good. Most synthetic fibers have the advantages of no mildew, no acid, alkali and weather resistance, and are easy to maintain.
5 Heat setting is generally better. Has melt porosity, heat shrinkability and thermoplasticity. The heat-setting treatment can reduce the heat shrinkability of the synthetic fiber fabrics, stabilize the size and shape, and improve shape retention. Colleagues can form stable pleats and other shapes.
6 Gloss is generally strong and dazzling, and can be controlled by humans.
Polyester
1. The source of polyester In 1946, polyester was first developed successfully in the United Kingdom with the trade name Terrellon. Polyester is China's brand name, a polyester fiber. At present, polyester is the world's largest and most widely used fiber.
2. Morphology of Polyester Polyester fabrics are longitudinally smooth and have a round cross-section. Polyester consists of short fibers and filaments. In the beginning, polyester mainly consisted of short fibers, including cotton, wool, and medium long, used in various blended or pure-spun fabrics. Common by the cotton and polyester, wool and polyester, linen, polyester sticky and other long products. Polyester filaments can be used to make warp-knitted fabrics, artificial silks such as soft yarns, georgettes, juliments, and fabrics. The low elasticity yarn can be made of fluffy, soft, breathable, knitted or woven fabrics with a hairy feel.
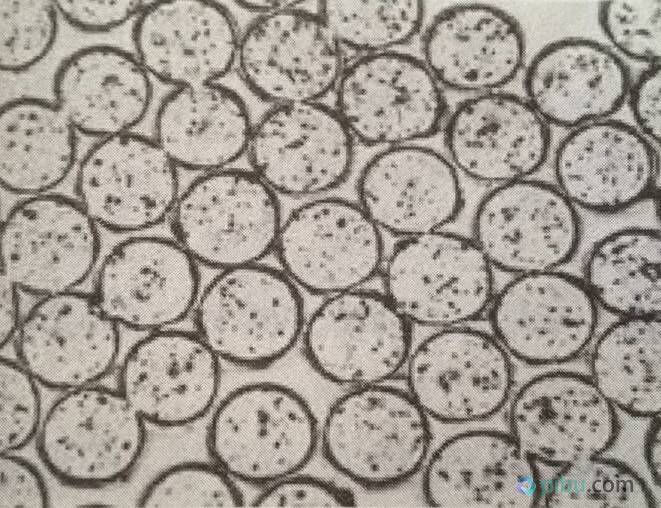

Polyester cross-section
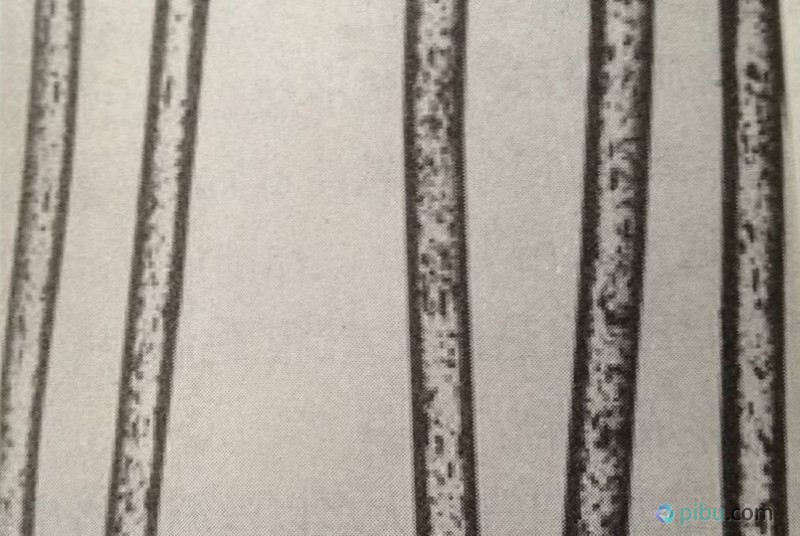

The longitudinal shape of polyester
3. Basic Properties of Polyester Polyester has an initial modulus of elasticity. The fabric is stiff, does not wrinkle, and is good in shape retention. It can maintain its original shape during processing and use, and heat setting can make polyester garments form a durable pleat. Polyester has poor hygroscopicity, the standard moisture regain is 0.4%, and it is not easy to dye. Special dyes, dyeing methods and equipment are required. Due to poor hygroscopicity and poor thermal conductivity, it is sultry to wear, and it is airtight, easy to accumulate static electricity, and easy to attract dust.
Polyester high strength, elongation, wear resistance, product durable. Its fabrics can be machine washed, shrink small and easy to wash and dry. Polyester is actually more stable to general chemistry and acid-resistant, but it is not resistant to concentrated alkali for long periods of high temperature treatment. Polyester treated with alkaline solution, the surface is easily corroded, the fibers become thinner, the weight is reduced, the hand feels better, the gloss is elegant, and has a silk style. This processing method becomes the alkali reduction treatment of polyester, and is the main component of polyester imitation silk. One of the methods. Polyester heat-resistant coins are generally high in chemical fiber, have a softening temperature of 230°C, an ironing temperature of 140 to 150°C, and a long-lasting ironing effect. Polyester lightfastness is second only to acrylic, and can be used in all seasons clothing, outdoor tooling, curtain fabrics and so on.
Nylon
1. The source of nylon Nylon was developed in the United States in 1939. The earliest clothing products were nylon socks. Nylon is a polyamide-based fiber that is currently used in many varieties and applications. Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 are the two most widely used polyamides.
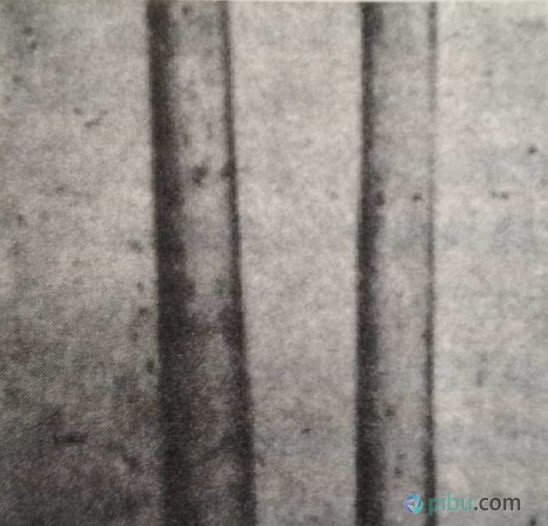
2. Morphology of Nylon The traditional nylon product is a straight, smooth, round, glossy filament. At present, nylon is still the main filament fabrics, ordinary nylon filament can be used for knitted fabrics and woven fabrics, high stretch yarn suitable for knitted stretch fabric. Nylon staple fiber yield is small, mainly wool short fiber, which can be blended with wool or other wool chemical fiber to improve the strength and wear resistance of the product.
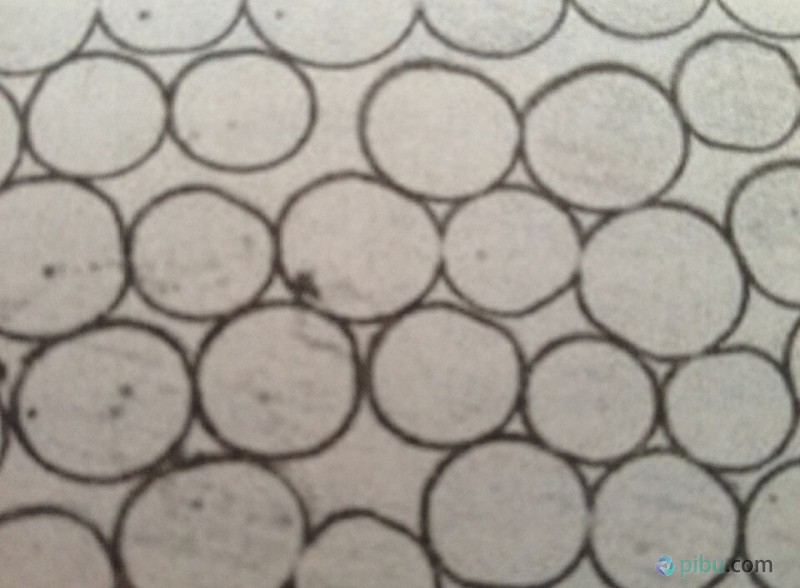
Nylon cross-section
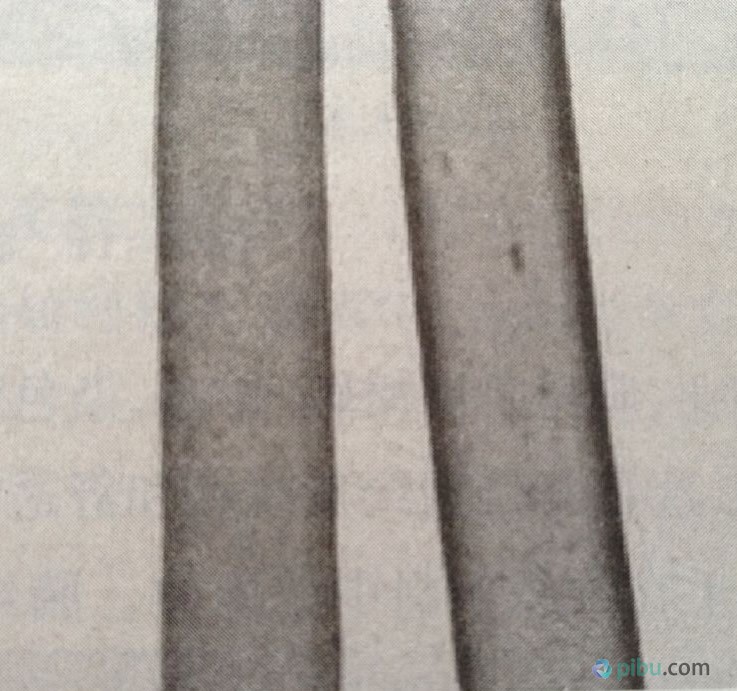
The longitudinal shape of nylon
3. The basic performance of nylon is good lung elasticity, good recovery, fabric is not easy to wrinkle. However, the fiber modulus is small, and very small Rashley can make the fabric deformed and deformed. The tremella has poor shape retention and the appearance is not stiff enough. Nylon moisture absorption is poor, the standard regain is 4¥, easy to static electricity, poor thermal conductivity, wearing more hot. Nylon has a relatively small relative density and is lightweight and suitable for mountaineering. Waterproof and windproof clothing, space suits, parachutes, etc. Nylon is the most prominent feature is good wear resistance, strength is the highest in the common fiber, its abrasion resistance is 10 times that of cotton, 20 times that of wool, commonly used to do socks, gloves, knitted sportswear and other wear-resistant fabrics. Nylon fabric can be machine washed and easy to wash and dry. Nylon tends to turn yellow at high temperatures. Drying at too high a temperature causes shrinkage and permanent wrinkles. Nylon is poor in lightfastness, yellowing in the sun, and reduced strength. Nylon heat resistance is not as good as polyester, and the ironing temperature is 120 ~ 130 °C. Polyamide is not resistant to acids and is sensitive to oxidants, especially chlorine-containing oxidants. Nylon is sensitive to naphthalenes, so the nylon fabric should not be placed in a hygienic ball (naphthalene).
Acrylic
1. Source of Acrylic Fiber In 1950, acrylic fiber was successfully opened by DuPont, USA. It was polyacrylonitrile obtained by copolymerizing acrylonitrile. The trade name consists of Orlon, Akroe, and Cashmere.
2. Morphology of Acrylic Fiber Acrylic is a smooth cylindrical column with a few grooves. Acrylic fibers are mainly short fibers, most of which are short wool fibers, used for pure spinning or blended with wool and other short hair fibers. The main products are acrylic fiber, yarn, knitwear, imitation fur fabrics. Medium and long acrylic fibers are often blended with polyester to make medium-length fabrics.

Acrylic cross-section

Acrylic longitudinal shape
3. The basic properties of acrylic fiber are soft, fluffy and warm. Many properties are similar to wool and are therefore called "synthetic wool." Compared with wool, acrylic fiber has the advantages of light weight, low cost, bright coloration, light resistance, no mildew, good wearability, etc. The disadvantage is that it is easy to pick up and pilling. This is an important factor in reducing the aesthetics and comfort of acrylic fibers, making it impossible for acrylic fibers to become a high-grade garment fabric, nor can it replace the position of wool in textile fabrics. Acrylic hygroscopicity is poor, the standard regain is 1.5% ~ 2%, easy to electrostatic, easy to attract dust. Acrylics have outstanding sunlight resistance and weather resistance. The best textile fibers are used in garments such as tents and curtains. Acrylic fiber is not as strong as polyester and other synthetic fibers, wear resistance and fatigue resistance is not very good, is a synthetic fiber durability is poor. Acrylics are resistant to weak acids and bases, but care must be taken when using strong bases and chlorine bleach. Ironing temperature is 130 ~ 140 °C.
Vinyl
1. The source of vinylon In 1950, vinylon fiber was industrialized in Japan. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber made from vinyl acetate was used as raw material.
2. Morphology of vinylon The vinylon is longitudinally straight, with 1 to 2 grooves. The cross section is waist-shaped and has a skin-core structure. The structure of the cortex is tight and the core structure is loose. The main products are cotton short fibers, often blended with cotton, used in bedding, military camouflage clothing, work clothes and so on.
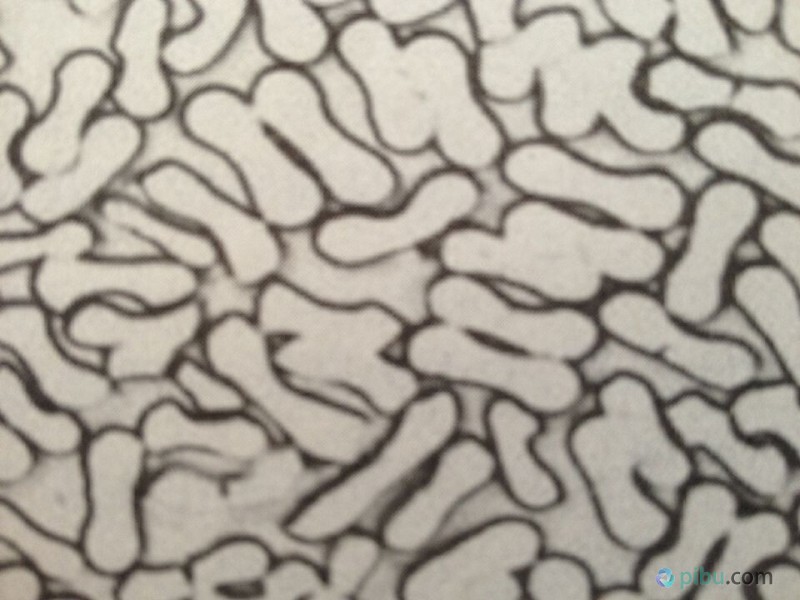
Vinylon cross-section
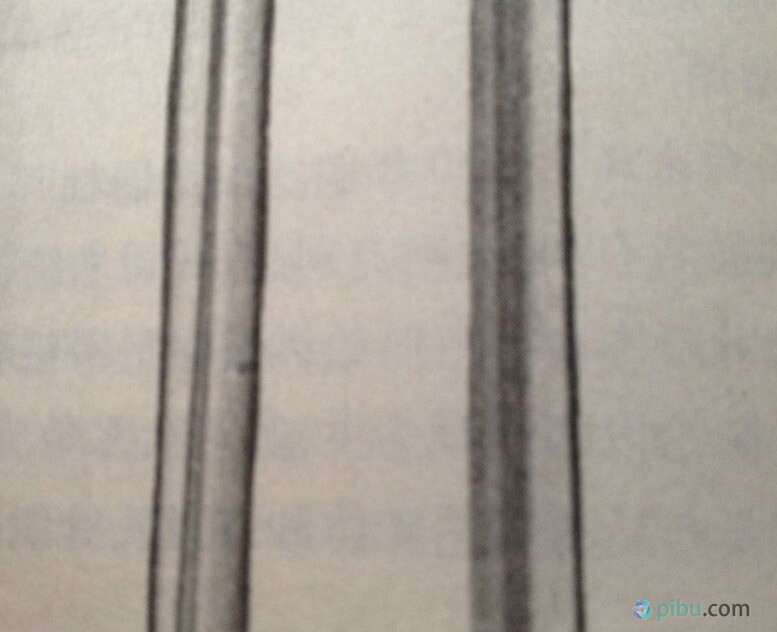
Vinylon's longitudinal form
3. Basic properties of vinylon The performance of vinylon is similar to that of cotton. The feel and appearance of vinylon fabric is like a cotton fabric, so it is called "synthetic cotton". Hygroscopicity is the best among the common synthetic fibers, and the moisture regain is 4.5% to 5% under normal atmospheric conditions. Vinylon's strength, elongation, and elasticity are worse than those of other synthetic fabrics, and fabrics are poor in shape retention and easy to wrinkle. Due to the presence of the skin core structure, the vinylon dyeability is not as good as that of cotton fibers and viscose, and the color is not bright, and it is not easy to dye evenly. Vinylon has strong chemical resistance, good sunlight resistance, good corrosion resistance, and no mildew. Vinylon has good dry heat resistance and is close to polyester. The ironing temperature is 120 ~ 140°C. Vinylon is poor in resistance to heat and humidity, so the water temperature during washing should not be too high. Do not spray water and wet cloth when ironing.
Polypropylene
1. Sources of Polypropylene Polypropylene in Italy was first industrialized in 1960 and was made from polypropylene melt spinning. Due to its low price and excellent performance, polypropylene has developed rapidly.
2. Polypropylene Morphology Polypropylene is smooth and straight in the longitudinal direction, and its cross section is mostly circular. Mainly consists of two types of filaments and staple fibers. Polypropylene filaments are commonly used in the production of silk and knitted fabrics. Polypropylene staple fiber production is less, and mostly cotton short fiber, commonly used in carpets, non-woven fabrics and other fabrics.
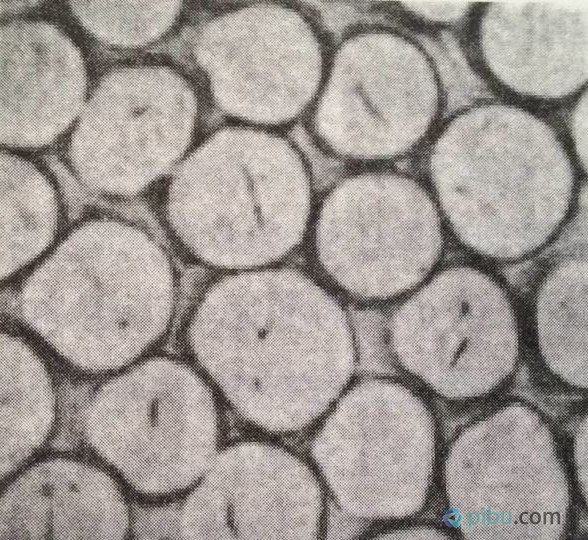
Polypropylene section shape

Polypropylene longitudinal shape
3. Basic properties of polypropylene Polypropylene has a waxy feel and luster, and is difficult to dye. Generally, it is dyed with the original liquid or modified. Polypropylene strength to engage in, good elasticity, good wear resistance, strong and durable, product recovery is good, stiff and easy to wrinkle, dimensional stability, good shape retention. Polypropylene density is small, only 0.91g/cm3, lighter than water, is the lightest textile fiber. Polypropylene is poor in hygroscopicity, moisture regain is zero, and static electricity and hairballs are easy to use during re-use and maintenance. After the polypropylene is made into microfibers, it has a strong wicking effect and can remove water vapor through capillary channels in the fibers to achieve the purpose of moisture permeability, so the comfort of the fabric is not bad. And since polypropylene itself is not hygroscopic, underwear made of polypropylene tidal fibers or diapers and other products not only deliver moisture, but also keep the skin dry. Polypropylene is poor in heat resistance, and it starts shrinking at temperatures above 100°C. The ironing temperature is between 90 and 100°C. It is best to use wet cloth or iron in the middle when ironing. Polypropylene has poor light and weather resistance, and is sensitive to ultraviolet rays. It is particularly susceptible to aging under the influence of water and oxygen. Fibers are easily reused, lose their luster during processing, and their strength and elongation decrease. As a result, the fibers become yellow and brittle, and therefore polypropylene Anti-aging treatment is usually performed. Polypropylene has good chemical stability, no influence on acid and alkali, and can withstand most chemical reagents. Therefore, it can be used for fishing nets, work clothes, and packaging bags.
Polychlorin
1. The source of the Kleenex Kleven is obtained by wet spinning or dry spinning from polyvinyl chloride or a copolymer containing more than 50% of polyvinyl chloride. The overseas market for Chloroplast is Tianmei, Lowell and other trade names. Since China was first successfully developed in Yunnan, it is also known as Polyester.
2. The morphological structure of the Kleenex Klein is longitudinally smooth or has 1 to 2 grooves and the cross section is nearly circular.
3. The basic properties of Kleenex Kleenex is poor in hygroscopicity, moisture regain is zero, dyeing is difficult, electrical insulation is strong, and a large number of negative charges are easily generated after the friction. Undergarments and other products made of it can be used to treat rheumatism. Arthritis is played by adjuvant therapy. Polyester fabrics have good elasticity and certain extensibility. The fabrics are not easy to wrinkle. Kleenex is flame-retardant, and it is the most non-flammable fiber in textile fibers. It is nearly softened by flame contraction, and it automatically extinguishes from the flame. Polychlorin has good chemical resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and general chemical reagents. Concentrated sulfuric acid is not easy. It can be used as a filter cloth for flowers on the square. The determination of Kleenex is poor heat resistance, it will shrink above 70 °C, the shrinkage in boiling water is greater, so intelligent and then 30 ~ 40 °C water washing, can not iron, not close to heating, hot water and other heat sources. Polyurethane is widely used in industry, such as for gas masks, insulating cloths, warehouses, etc. Mainly in the civil use mainly silk and staple fiber, silk yarn can be used to produce screens, screens, ropes, bags, etc., short fibers can be used to make underwear, decorative cloth and so on.
Spandex
1. The source of spandex Spandex was developed by DuPont in 1945. Its trade name is Lycra, also known as Spandex, which is a highly elastic fiber.
2. Spandex morphological structure Spandex is mostly white opaque extinction filaments. The vertical surface is dark and unclear. The cross-section presents different shapes due to different production processes. The cross-sections of dry-spinning spandex are round, oval and peanut-shaped. The wet-spinning spandex is mainly of coarse leaf shape and irregular shape, and between the various filaments. The longitudinally formed irregular adhesive dots form a cohesive multifilament; the melt-spinning spandex is mainly a monofilament or multifilament of circular cross-section.
3. The basic properties of spandex The most important feature of spandex is high elasticity and high recovery. Its elongation at break can reach 450% ~ 800%, the elongation recovery rate can reach 90%, and the retractive force at the time of rebound is less than the stretching force, so it is comfortable to wear, there is no oppressive feeling of rubber filament, but with the common fiber In comparison, the intensity is lower. Spandex is poor in hygroscopicity, and the moisture regain is 0.8% to 1% under normal atmospheric conditions. Spandex has good properties such as acid resistance, alkali resistance, and light resistance, but its heat resistance is poor. Spandex appears in products mainly in the form of core-spun yarns or in combination with other fibers, and as long as very little spandex is used, excellent elasticity can be brought into the fabric to improve dimensional stability and shape retention. At present, spandex is widely used in stretch fabrics, sportswear, socks and other products.
1 The fiber uniformity is good, and the length, fineness, and cross-sectional morphology can be controlled as needed. Different cross-section fibers produce different properties such as gloss, durability and warmth retention.
2 Poor hygroscopicity, fabrics are easy to wash and dry, no shrinkage, good washability, but not as hot and humid comfort as natural fibers, easy to electrostatic, easy to attract dust.
3 Most synthetic fibers have strong strength, large elongation capacity, good elasticity, good abrasion resistance, and they are made of durable, good conformability and are not easy to wrinkle. Synthetic fiber filament fabric is easy to hook silk, synthetic fiber staple fiber fabric is easy to pilling.
4 The chemical stability is good. Most synthetic fibers have the advantages of no mildew, no acid, alkali and weather resistance, and are easy to maintain.
5 Heat setting is generally better. Has melt porosity, heat shrinkability and thermoplasticity. The heat-setting treatment can reduce the heat shrinkability of the synthetic fiber fabrics, stabilize the size and shape, and improve shape retention. Colleagues can form stable pleats and other shapes.
6 Gloss is generally strong and dazzling, and can be controlled by humans.
Polyester
1. The source of polyester In 1946, polyester was first developed successfully in the United Kingdom with the trade name Terrellon. Polyester is China's brand name, a polyester fiber. At present, polyester is the world's largest and most widely used fiber.
2. Morphology of Polyester Polyester fabrics are longitudinally smooth and have a round cross-section. Polyester consists of short fibers and filaments. In the beginning, polyester mainly consisted of short fibers, including cotton, wool, and medium long, used in various blended or pure-spun fabrics. Common by the cotton and polyester, wool and polyester, linen, polyester sticky and other long products. Polyester filaments can be used to make warp-knitted fabrics, artificial silks such as soft yarns, georgettes, juliments, and fabrics. The low elasticity yarn can be made of fluffy, soft, breathable, knitted or woven fabrics with a hairy feel.

Polyester cross-section

The longitudinal shape of polyester
3. Basic Properties of Polyester Polyester has an initial modulus of elasticity. The fabric is stiff, does not wrinkle, and is good in shape retention. It can maintain its original shape during processing and use, and heat setting can make polyester garments form a durable pleat. Polyester has poor hygroscopicity, the standard moisture regain is 0.4%, and it is not easy to dye. Special dyes, dyeing methods and equipment are required. Due to poor hygroscopicity and poor thermal conductivity, it is sultry to wear, and it is airtight, easy to accumulate static electricity, and easy to attract dust.
Polyester high strength, elongation, wear resistance, product durable. Its fabrics can be machine washed, shrink small and easy to wash and dry. Polyester is actually more stable to general chemistry and acid-resistant, but it is not resistant to concentrated alkali for long periods of high temperature treatment. Polyester treated with alkaline solution, the surface is easily corroded, the fibers become thinner, the weight is reduced, the hand feels better, the gloss is elegant, and has a silk style. This processing method becomes the alkali reduction treatment of polyester, and is the main component of polyester imitation silk. One of the methods. Polyester heat-resistant coins are generally high in chemical fiber, have a softening temperature of 230°C, an ironing temperature of 140 to 150°C, and a long-lasting ironing effect. Polyester lightfastness is second only to acrylic, and can be used in all seasons clothing, outdoor tooling, curtain fabrics and so on.
Nylon
1. The source of nylon Nylon was developed in the United States in 1939. The earliest clothing products were nylon socks. Nylon is a polyamide-based fiber that is currently used in many varieties and applications. Nylon 6 and Nylon 66 are the two most widely used polyamides.
2. Morphology of Nylon The traditional nylon product is a straight, smooth, round, glossy filament. At present, nylon is still the main filament fabrics, ordinary nylon filament can be used for knitted fabrics and woven fabrics, high stretch yarn suitable for knitted stretch fabric. Nylon staple fiber yield is small, mainly wool short fiber, which can be blended with wool or other wool chemical fiber to improve the strength and wear resistance of the product.

Nylon cross-section

The longitudinal shape of nylon
3. The basic performance of nylon is good lung elasticity, good recovery, fabric is not easy to wrinkle. However, the fiber modulus is small, and very small Rashley can make the fabric deformed and deformed. The tremella has poor shape retention and the appearance is not stiff enough. Nylon moisture absorption is poor, the standard regain is 4¥, easy to static electricity, poor thermal conductivity, wearing more hot. Nylon has a relatively small relative density and is lightweight and suitable for mountaineering. Waterproof and windproof clothing, space suits, parachutes, etc. Nylon is the most prominent feature is good wear resistance, strength is the highest in the common fiber, its abrasion resistance is 10 times that of cotton, 20 times that of wool, commonly used to do socks, gloves, knitted sportswear and other wear-resistant fabrics. Nylon fabric can be machine washed and easy to wash and dry. Nylon tends to turn yellow at high temperatures. Drying at too high a temperature causes shrinkage and permanent wrinkles. Nylon is poor in lightfastness, yellowing in the sun, and reduced strength. Nylon heat resistance is not as good as polyester, and the ironing temperature is 120 ~ 130 °C. Polyamide is not resistant to acids and is sensitive to oxidants, especially chlorine-containing oxidants. Nylon is sensitive to naphthalenes, so the nylon fabric should not be placed in a hygienic ball (naphthalene).
Acrylic
1. Source of Acrylic Fiber In 1950, acrylic fiber was successfully opened by DuPont, USA. It was polyacrylonitrile obtained by copolymerizing acrylonitrile. The trade name consists of Orlon, Akroe, and Cashmere.
2. Morphology of Acrylic Fiber Acrylic is a smooth cylindrical column with a few grooves. Acrylic fibers are mainly short fibers, most of which are short wool fibers, used for pure spinning or blended with wool and other short hair fibers. The main products are acrylic fiber, yarn, knitwear, imitation fur fabrics. Medium and long acrylic fibers are often blended with polyester to make medium-length fabrics.

Acrylic cross-section

Acrylic longitudinal shape
Vinyl
1. The source of vinylon In 1950, vinylon fiber was industrialized in Japan. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber made from vinyl acetate was used as raw material.
2. Morphology of vinylon The vinylon is longitudinally straight, with 1 to 2 grooves. The cross section is waist-shaped and has a skin-core structure. The structure of the cortex is tight and the core structure is loose. The main products are cotton short fibers, often blended with cotton, used in bedding, military camouflage clothing, work clothes and so on.

Vinylon cross-section

Vinylon's longitudinal form
3. Basic properties of vinylon The performance of vinylon is similar to that of cotton. The feel and appearance of vinylon fabric is like a cotton fabric, so it is called "synthetic cotton". Hygroscopicity is the best among the common synthetic fibers, and the moisture regain is 4.5% to 5% under normal atmospheric conditions. Vinylon's strength, elongation, and elasticity are worse than those of other synthetic fabrics, and fabrics are poor in shape retention and easy to wrinkle. Due to the presence of the skin core structure, the vinylon dyeability is not as good as that of cotton fibers and viscose, and the color is not bright, and it is not easy to dye evenly. Vinylon has strong chemical resistance, good sunlight resistance, good corrosion resistance, and no mildew. Vinylon has good dry heat resistance and is close to polyester. The ironing temperature is 120 ~ 140°C. Vinylon is poor in resistance to heat and humidity, so the water temperature during washing should not be too high. Do not spray water and wet cloth when ironing.
Polypropylene
1. Sources of Polypropylene Polypropylene in Italy was first industrialized in 1960 and was made from polypropylene melt spinning. Due to its low price and excellent performance, polypropylene has developed rapidly.
2. Polypropylene Morphology Polypropylene is smooth and straight in the longitudinal direction, and its cross section is mostly circular. Mainly consists of two types of filaments and staple fibers. Polypropylene filaments are commonly used in the production of silk and knitted fabrics. Polypropylene staple fiber production is less, and mostly cotton short fiber, commonly used in carpets, non-woven fabrics and other fabrics.

Polypropylene section shape

Polypropylene longitudinal shape
3. Basic properties of polypropylene Polypropylene has a waxy feel and luster, and is difficult to dye. Generally, it is dyed with the original liquid or modified. Polypropylene strength to engage in, good elasticity, good wear resistance, strong and durable, product recovery is good, stiff and easy to wrinkle, dimensional stability, good shape retention. Polypropylene density is small, only 0.91g/cm3, lighter than water, is the lightest textile fiber. Polypropylene is poor in hygroscopicity, moisture regain is zero, and static electricity and hairballs are easy to use during re-use and maintenance. After the polypropylene is made into microfibers, it has a strong wicking effect and can remove water vapor through capillary channels in the fibers to achieve the purpose of moisture permeability, so the comfort of the fabric is not bad. And since polypropylene itself is not hygroscopic, underwear made of polypropylene tidal fibers or diapers and other products not only deliver moisture, but also keep the skin dry. Polypropylene is poor in heat resistance, and it starts shrinking at temperatures above 100°C. The ironing temperature is between 90 and 100°C. It is best to use wet cloth or iron in the middle when ironing. Polypropylene has poor light and weather resistance, and is sensitive to ultraviolet rays. It is particularly susceptible to aging under the influence of water and oxygen. Fibers are easily reused, lose their luster during processing, and their strength and elongation decrease. As a result, the fibers become yellow and brittle, and therefore polypropylene Anti-aging treatment is usually performed. Polypropylene has good chemical stability, no influence on acid and alkali, and can withstand most chemical reagents. Therefore, it can be used for fishing nets, work clothes, and packaging bags.
Polychlorin
1. The source of the Kleenex Kleven is obtained by wet spinning or dry spinning from polyvinyl chloride or a copolymer containing more than 50% of polyvinyl chloride. The overseas market for Chloroplast is Tianmei, Lowell and other trade names. Since China was first successfully developed in Yunnan, it is also known as Polyester.
2. The morphological structure of the Kleenex Klein is longitudinally smooth or has 1 to 2 grooves and the cross section is nearly circular.
3. The basic properties of Kleenex Kleenex is poor in hygroscopicity, moisture regain is zero, dyeing is difficult, electrical insulation is strong, and a large number of negative charges are easily generated after the friction. Undergarments and other products made of it can be used to treat rheumatism. Arthritis is played by adjuvant therapy. Polyester fabrics have good elasticity and certain extensibility. The fabrics are not easy to wrinkle. Kleenex is flame-retardant, and it is the most non-flammable fiber in textile fibers. It is nearly softened by flame contraction, and it automatically extinguishes from the flame. Polychlorin has good chemical resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and general chemical reagents. Concentrated sulfuric acid is not easy. It can be used as a filter cloth for flowers on the square. The determination of Kleenex is poor heat resistance, it will shrink above 70 °C, the shrinkage in boiling water is greater, so intelligent and then 30 ~ 40 °C water washing, can not iron, not close to heating, hot water and other heat sources. Polyurethane is widely used in industry, such as for gas masks, insulating cloths, warehouses, etc. Mainly in the civil use mainly silk and staple fiber, silk yarn can be used to produce screens, screens, ropes, bags, etc., short fibers can be used to make underwear, decorative cloth and so on.
Spandex
1. The source of spandex Spandex was developed by DuPont in 1945. Its trade name is Lycra, also known as Spandex, which is a highly elastic fiber.
2. Spandex morphological structure Spandex is mostly white opaque extinction filaments. The vertical surface is dark and unclear. The cross-section presents different shapes due to different production processes. The cross-sections of dry-spinning spandex are round, oval and peanut-shaped. The wet-spinning spandex is mainly of coarse leaf shape and irregular shape, and between the various filaments. The longitudinally formed irregular adhesive dots form a cohesive multifilament; the melt-spinning spandex is mainly a monofilament or multifilament of circular cross-section.
3. The basic properties of spandex The most important feature of spandex is high elasticity and high recovery. Its elongation at break can reach 450% ~ 800%, the elongation recovery rate can reach 90%, and the retractive force at the time of rebound is less than the stretching force, so it is comfortable to wear, there is no oppressive feeling of rubber filament, but with the common fiber In comparison, the intensity is lower. Spandex is poor in hygroscopicity, and the moisture regain is 0.8% to 1% under normal atmospheric conditions. Spandex has good properties such as acid resistance, alkali resistance, and light resistance, but its heat resistance is poor. Spandex appears in products mainly in the form of core-spun yarns or in combination with other fibers, and as long as very little spandex is used, excellent elasticity can be brought into the fabric to improve dimensional stability and shape retention. At present, spandex is widely used in stretch fabrics, sportswear, socks and other products.
Face recognition is a biometric technology based on facial feature information.A series of related technologies,also known as portrait recognition and face recognition,that use cameras or cameras to collect images or video streams containing faces,and automatically detect and track faces in the images,and then perform face recognition on the detected faces.The Recognition Lens plays a significant role in the face recognition system.
Recognition Lens,Digital Projection Lens,Distortion Recognition Lens,Optical Infrared Lens
Dongguan Shengqiang Electronic Co.,Ltd , https://www.sqoptical.com